CCITcoder
Contents
Introduction to Java
DataType and Operation
Conditional statements
Iterative statements
Functions
OOPs
- OOPs
- Object
- Access Specifiers
- Methods Returning Value
- Nesting of methods
- method Overloading
- Constructor
- Constructor Overloading
- Immutablemmutable Objects
String
Static Data members
Inherintance
- Inherintance
- Method Overriding
- calling base method
- Constructors and Inheritance
- Types of Inheritance
- Single Inhertance
- Multi-level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
Polymorphisam
Applets
AWT
- AWT
- Class Frame
- Class Button
- Event Delegation Modal
- Class TextField
- Class TextArea
- Class Label
- Class Component
- Class Container
- Class Checkbox
- Class List
- Class Choice
- Class FlowLayout
- Class BorderLayout
- Class GridLayout
- Class CardLayout
- Class Panel
- Class Font
- Menus
- Mouse Events
- Window Events
MultiThreading
I/o
Exception Handling
Collection FrameWork
Contents
Introduction to Java
DataType and Operation
Conditional statements
Iterative statements
Functions
OOPs
- OOPs
- Object
- Access Specifiers
- Methods Returning Value
- Nesting of methods
- method Overloading
- Constructor
- Constructor Overloading
- Immutablemmutable Objects
String
Static Data members
Inherintance
- Inherintance
- Method Overriding
- calling base method
- Constructors and Inheritance
- Types of Inheritance
- Single Inhertance
- Multi-level Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
Polymorphisam
Applets
AWT
- AWT
- Class Frame
- Class Button
- Event Delegation Modal
- Class TextField
- Class TextArea
- Class Label
- Class Component
- Class Container
- Class Checkbox
- Class List
- Class Choice
- Class FlowLayout
- Class BorderLayout
- Class GridLayout
- Class CardLayout
- Class Panel
- Class Font
- Menus
- Mouse Events
- Window Events
MultiThreading
I/o
Exception Handling
Collection FrameWork
Collections Framework
Collections Framework Package: java.util
- The Java collections framework provides a set of interfaces and classes to implement various data structures and algorithms.
- Java Collections can achieve all the operations that you perform on a data such as searching, sorting, insertion, manipulation, and deletion.
- Java Collection framework provides
- interfaces (Set, List, Queue, Deque)
- classes (ArrayList, Vector, LinkedList, PriorityQueue, HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSet).
- Advantages
- Reduces programming effort
- Increases program speed.
- Reduces effort to learn and to use new APIs
Hierarchy of Collection Framework
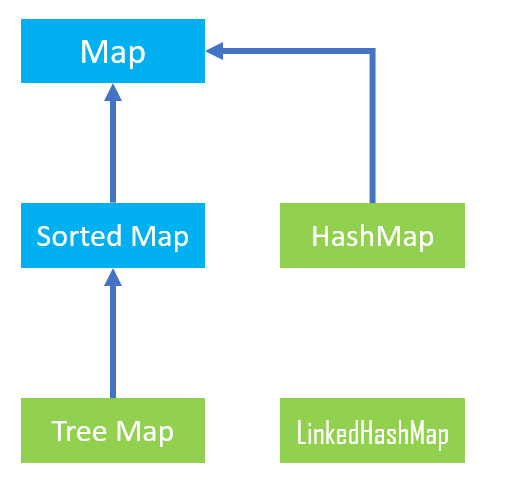
.png)
Collection Interface
- The Collection interface is the root interface of the Java collections framework.
- There are three interface implement List, set and Queue.
- Collection is group of objects.
- This interface defines the standard which must be followed by all collection type of objects.
- public boolean add(Object obj)
- to add an element.
- public boolean addAll(Collection c)
- to add all elements of collection.
- public boolean remove(Object element)
- to delete an element.
- public int size()
- It returns the total number of elements.
- public void clear()
- removes all elements.
- public boolean removeAll(Collection c)
- to delete all the elements present in specified collection.
- public boolean retainAll(Collection c)
- to delete all the elements except the specified collection.
- public boolean contains(Object element)
- It is used to search an element.
- public Iterator iterator()
- It returns an iterator.
- public Object[ ] toArray()
- It converts collection into array.
- public boolean isEmpty()
- It checks if collection is empty.
List Interface
- It defines Standard for ordered collection.
- List Interface is implemented by ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector and Stack classes.
- void add(int index, Object obj)
- Inserts obj into the list at the index.
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection c)
- Inserts all elements of c into the list at the index.
- Object remove(int index)
- Removes the element at position index list and returns the deleted element.
- Object set(int index, Object obj)
- Sets object at the location.
- It returns the replaced element.
- Object get(int index)
- Returns the object stored at the specified index.
- int indexOf(Object obj)
- Returns the index of the first instance of obj.
- If obj is not in list, -1 is returned.
- int lastIndexOf(Object obj)
- Returns the index of the last instance of obj.
- If obj is not in list, -1 is returned.
- ListIterator listIterator( )
- Returns an iterator to the start of the list.
- ListIterator listIterator(int index)
- Returns an iterator to the list that begins at the specified index.
- List subList(int start, int end)
- Returns a list that includes elements from start to end-1 in the list.